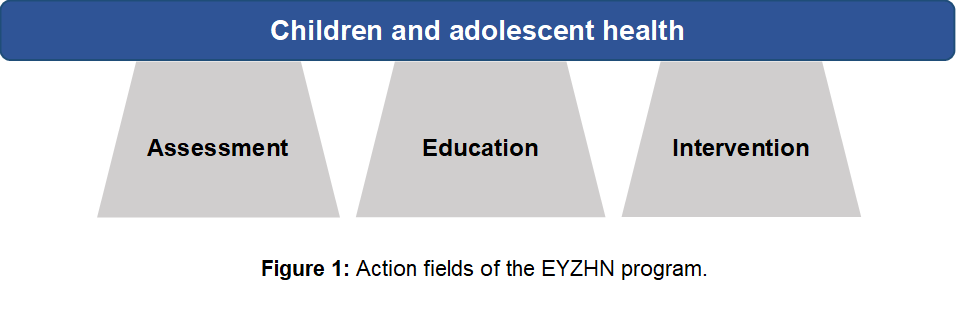
The EYZHN program (National Action for Children’s Health) is a nationwide school-based health-promotion initiative implemented in Greece from 2012 to 2017 under the auspices of Harokopio University of Athens, Greece and the Greek Ministry of Education, Research and Religious Affairs. EYZHN aimed at promoting a healthy lifestyle and ultimately establishing good health among the paediatric school population of Greece. The program included three major action fields (Figure 1): the “assessment” action field, aiming at evaluating – at an annual basis – the lifestyle and growth status of Greek schoolchildren; the “education” action field, aiming at providing evidence-based information about growth, lifestyle and health to students, parents, teachers and health-care professionals; and the “intervention” action field, aiming at promoting the principles of a healthy lifestyle, with emphasis on the Mediterranean pattern, though multicomponent activities.
The EYZHN program (National Action for Children’s Health) is a nationwide school-based health-promotion initiative implemented in Greece from 2012 to 2017 under the auspices of Harokopio University of Athens, Greece and the Greek Ministry of Education, Research and Religious Affairs. EYZHN aimed at promoting a healthy lifestyle and ultimately establishing good health among the paediatric school population of Greece. The program included three major action fields (Figure 1): the “assessment” action field, aiming at evaluating – at an annual basis – the lifestyle and growth status of Greek schoolchildren; the “education” action field, aiming at providing evidence-based information about growth, lifestyle and health to students, parents, teachers and health-care professionals; and the “intervention” action field, aiming at promoting the principles of a healthy lifestyle, with emphasis on the Mediterranean pattern, though multicomponent activities.
The “Assessment” action field of the ΕΥΖΗΝ program was implemented in Primary and Secondary schools of Greece in cooperation with the Greek Ministry of Education, Research and Religious Affairs. Approximately 4,000 schools participated annually and over 1,200,000 students in total were evaluated in terms of anthropometric indices, dietary, physical activity and sleep habits, as well as physical fitness level. The results of the aforementioned evaluation were given to parents as a report to increase their awareness of the health status of their children.
According to the pooled results of this nationwide health survey, childhood obesity is a major public health problem in Greece, given that ~35% of the pediatric population was overweight or obese according to international standards. Specifically, 25% and 10% of the students were classified as overweight and obese, respectively, with boys presenting higher rates of obesity compared to girls (11% versus 9%). The problem of excess adiposity was mainly detected at 8–11-year-old children, and almost 4 out of 10 students who were in the onset of puberty were overweight or obese. The regions of Greece with the highest rates of overweight or obese children were those of the Southern Aegean (38%), North Aegean (37%) and the Ionian Islands (35%), while the lowest rates were observed in the regions of Epirus (30%), West Greece (30%) and Thessaly (31%). At the same time, a significant proportion of Greek schoolchildren did not meet current guidelines on a healthy lifestyle, since only half of them adequately adopted the healthy Mediterranean diet and were sufficiently physically active, while 1 in 4 students reported inadequate sleep duration and low physical fitness level (cardiorespiratory capacity, strength, agility, etc.).
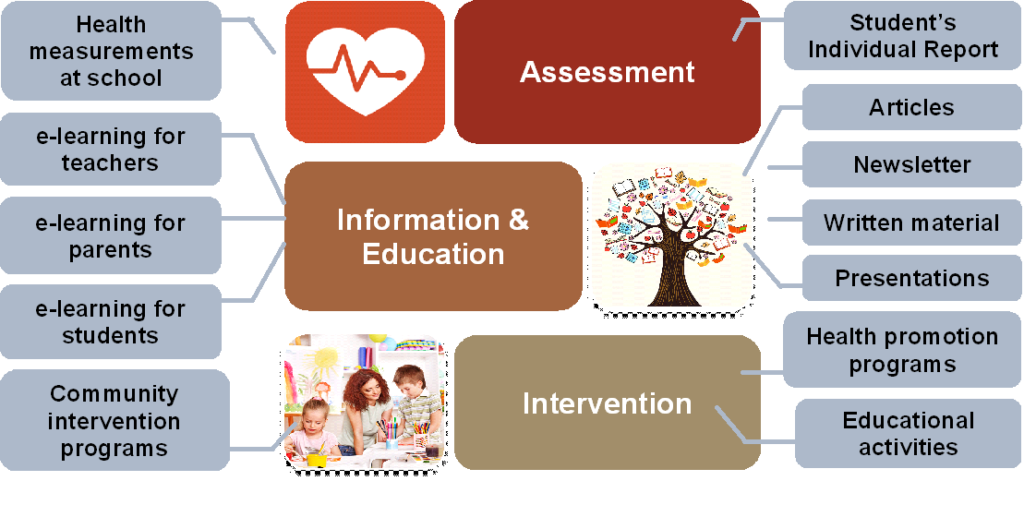
Based on the aforementioned observations, it is clear that childhood obesity remains a major public health issue in Greece and that students’ dietary, physical activity and sleep habits are far from international recommendations. To this end, the ΕΥΖΗΝ program also included several informative, educational and interventional actions regarding childhood weight status, nutrition, physical activity and health. The aim of these actions was to provide stimuli to the general population (children, parents, teachers and health professionals) towards adopting the principles of a healthy lifestyle. The figure below depicts the various actions included in each of the ΕΥΖΗΝ action fields.